WHAT IS OBDII?
OBDII stands for Second Generation "On Board Diagnostics". The system is incorporated into the computers of all new vehicles from 1996 on, that weigh less than 14,000 lbs. This includes passenger cars, pickup trucks, and sport utility vehicles. The OBDII system monitors virtually every fuel & emission related component on the vehicle that can affect the emission performance. This ensures that the vehicle remains environmentally friendly over the entire life of the vehicle and assists repair technicians when diagnosing emission related problems. If a problem is detected, the OBDII system illuminates a warning light on the instrument panel to let the driver know that there is a malfunction and that service is required to fix the problem. The OBDII system stores the information so the technician can accurately find and fix the problem.
HOW DOES OBDII DIFFER FROM OBDI?
OBDI was the first generation "On Board Diagnostics" system. It was required on 1991 and newer vehicles and monitored fewer emission components than OBDII. OBDI components were not calibrated to specific emission performance levels and OBDI did not monitor the catalytic converter performance. This made OBDI less effective at helping service technicians diagnose and fix emission problems.
WHY IS OBDII NEEDED?
Today's new vehicles have the cleanest running engines and the lowest emissions in the world. The emission quality is a result of a complex system of components that all need to be working together and functioning properly. If any component fails or deteriorates over time, then the emissions can quickly increase to unacceptable levels. OBDII is always "ON" and will alert the driver as soon as a failure occurs. This gives the technician the best opportunity to find and fix the problem early before severe and expensive damage is done to other components that make up the emission system.
HOW DOES OBDII WORKS?
OBDII monitors electrical impulses from several emission components and compares the data to determine if they are functioning properly. Oxygen sensors before and after the catalytic converter measure the catalytic converter's performance. Spacing between components such as fuel injectors and the oxygen sensors is important because OBDII calculates the time and movement of exhaust gasses through the system when making comparisons.
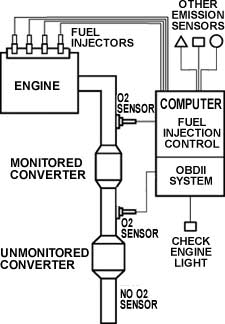 The readings taken from the front oxygen sensor are compared with readings from a rear oxygen sensor to determine how the monitored converter between the sensors is functioning. The readings taken from the front oxygen sensor are compared with readings from a rear oxygen sensor to determine how the monitored converter between the sensors is functioning.
Unmonitored converters may be positioned behind the rear oxygen sensor for a final cleanup of any harmful emissions that escaped the front converters.
OBDII is integrated with the fuel delivery system to keep the engine operating a peak efficiency. It is important to have a vehicle serviced as soon as possible when the OBDII system's warning light comes on. Emission system problems could impact engine performance, fuel economy and could also lead to the failure of other more expensive emission components such as the converter(s).
OBDII stores information on how the vehicle's emission system was malfunctioning when the warning light was activated. These codes can be retrieved by the technician to help accurately diagnose the problem and expedite the repair process.
|